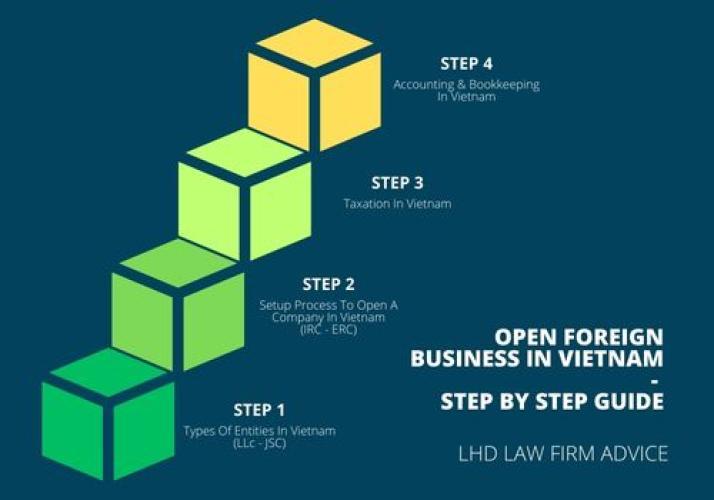
Doing Business In Vietnam
- 01/12/2025

→ Doing business in vietnam advise by Experts at Vietnam LLC setup ► Set up a wholly foreign-owned entity, joint venture, public limited company, branch or representative office ☏ +840907996249 or email: all@lhdfirm.com
 CONTENT
CONTENT
 CONTENT
CONTENT
☆ An Introduction to Doing Business in Vietnam 2022 – New Publication from LHD Law Firm
WHY DOING BUSINESS IN VIETNAM ?
Vietnam has many competitive advantages when it comes to being an attractive destination for foreign investment, whose booming economy offers a lot of investment opportunities. Here are reasons why you should invest in Vietnam

We advise and represent clients to carry out the following issues
Consulting policies, conditions, schedules and procedures with investment activities in Vietnam.
Consulting investment forms consistent with needs, aims and capabilities of our clients.
Representing clients with preparation of dossiers and documents and liaising to competent authorities for implement of procedures of investment registration and investment project evaluation the laws.
Representing clients on negotiation with their partners with regard to their needs of investment, cooperation, assignment/receipt of assignment of project.

We advise and represent clients to carry out the following issues
- Consulting on establishing enterprises including
- Advise for choosing the best type of business following the company’s goals and missions.
- Advice for business operations: consultant experts will consult on choosing, arranging business operations scientifically and in suitable way with the state law and the business’ will.
- Business registration certificate including: Business registration; Legal entity stamp;
- Tax code registration.
- Setting up branches and representative offices.
- Modifying business registration content.
- Business organizing, re-arranging procedures (M&A) and other related issues.
Starting a Business in Vietnam
There are 10 procedures to undertake when starting a business in Vietnam, making it among the most complex start-up environments in the world. What’s more, many tasks facing new corporate entities may be unfamiliar to overseas companies, making the task far more rigorous. Registration of the seal-sample at the Police Department, for example, or publically announcing the formation in a local newspaper are procedures most companies generally don’t have to complete.
Dealing with Construction Permits
It takes 110 days and 11 procedures to get permits for construction in Vietnam, once again requiring interaction with several official departments. Inspections must be carried out by the Department of Construction and the municipality, and certificates should be obtained from the Firefighters Prevention Department, the Department of Construction and the Department of Natural Resources and Environment.
Getting Electricity
Getting electrical connection is among the most rigorous tasks facing startups in Vietnam, taking 115 days to complete and costing a significant percentage of income per capita. Inspections by the local power corporation are required before completing processes with the Traffic and Transport Department and the Firefighters Prevention Department.
Registering Property
Registering property takes 57 days to complete, which is far higher than the OECD norm but around average for East Asia and Pacific. Contracts between the transferor and the transferee are signed before taxation is paid and registration for the right to use land is complete.
Getting Credit
Vietnam is home to quite a stable credit environment, and obtaining capital is a relatively smooth process for businesses. However, the lack of a private credit bureau can make the process a little trickier for overseas firms.
Protecting Investors
Investor protection is an area in which Vietnam fails miserably. It is ranked in 169th place by the World Bank and IFC, with a weak director liability index and shareholder suits index.
Paying Taxes
There are a massive 32 corporate tax payments to be made each year which takes an average of 872 company hours to complete. Compared to the OECD norm of 176 and the East Asia and Pacific average of 209, taxation is one of the most burdensome processes of doing business in Vietnam.
Trading Across Borders
Given its strong manufacturing base and reliance on interconnectivity, trading across borders is a cheap endeavour. However, that isn’t to say the process is not complicated, and the stream of documentation required for both importing and exporting highlights that cross-border trade can be difficult at the best of times.
Enforcing Contracts and Resolving Insolvency
Enforcing contracts takes 400 days to complete and 34 procedures. Resolving insolvency is a far more laborious process, taking five years on average to complete and with a low recovery rate.
Culture
The Vietnamese believe in the teachings of the early Chinese philosopher Confucius which emphasise the importance of relationships, responsibility and obligation. Vietnam is also a collectivist country and community concerns will almost always come before business or individual needs.
Doing business in Viet Nam – Opportunities and Threats 2022 - Advise by LHD Law Firm
Vietnam Becomes The New Southeast Asian Tiger economy. There are many investors around the world choosing Vietnam for their business plans. Doing Business in Vietnam still has socio-economic characteristics that create opportunities and threats for investment activities for foreigners.
Vietnam is a dynamic market in the Asia - Pacific region. Although it has only been open to business to the rest of the world for a few decades, people's cultural and entrepreneurial trends have quickly revived its economy. Doing Business in Vietnam is expanded to a variety of fields and industries. However, the characteristics of intellectual property, legal and cybersecurity in here still pose certain challenges for foreign invest.
Top 10 largest companies in Vietnam were selected by LHD Law Firm based on their size, credit ratings, and business performance in 2022 and More ...
1. SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS VIETNAM COMPANY LIMITED
In 2017, the sales of Samsung Electronics Vietnam Company Limited reached USD 58 billion, and this figure was USD 65.7 billion in 2018, accounting for 28% of Vietnam’s GDP. This business has maintained the No. 1 position in the list of the largest companies in Vietnam.
Samsung employs more than 100,000 people. It has helped Vietnam become the second largest exporter of smartphones in the world, following China.
2. VIETNAM ELECTRICITY
Vietnam Electricity (EVN) is a premium state-owned enterprise in Vietnam. Before September 2006, this group was known as Vietnam Electricity Corporation, a state-owned corporation managed by the central government.
EVN core business activities are production, transmission and import-export of electricity. The Group also builds power generation plants, electricity distribution grid systems to households, manages the national grid, and exports and imports electricity to and from neighboring countries such as China and Laos.
3. BINH SON REFINING AND PETROCHEMICAL JOINT STOCK COMPANY
Binh Son Refining and Petrochemical Joint Stock Company (BSR) is a member unit of the Vietnam Oil and Gas Group assigned to manage and operate Dung Quat oil refinery. It plays a leading role in and sets the foundation for the development of the petrochemical industry in Vietnam.
Dung Quat Oil Refinery Plant is a national key project with a total investment of over USD 3 billion. Its processing capacity is 6.5 million tons of crude oil per year.
4. MOBILE WORLD JOINT STOCK COMPANY
Formerly known as Mobile World Co., Ltd. founded in 2004, Mobile World Joint Stock Company (MWG) was established on January 16, 2009. The company is the biggest retailer in Vietnam by size, revenue and profit.
MWG is holding a 45% mobile phone market share and s 35% electronics market share in Vietnam with 1,800 stores around Vietnam.
5. DOJI GOLD & GEMS GROUP JOINT STOCK COMPANY
Doji Gold & Gems Group Joint Stock Company, formerly known as TTD Trading and Technology Development Company, was established on July 28, 1994. In the 90s, TTD Company was the pioneer enterprise specializing in gem mining, cutting, grinding and exporting gemstones to the international market.
In 2007, TTD Company officially changed its name to Doji Gold & Gems Group Joint Stock Company.
6. VIETTEL GROUP
Viettel Group was established under Decision 2079/2009/QD-TTg signed on December 14, 2009 by the Prime Minister. It is a 100% state-owned economic and defense enterprise with charter capital of VND 121,520 billion.
Viettel is the largest telecommunication and information technology group in Vietnam, and is considered one of the fastest growing telecommunications companies in the world. Currently, Viettel is investing in 7 countries in 3 continents including Asia, America, and Africa.
7. NGHI SON REFINERY AND PETROCHEMICAL LIMITED LIABILITY COMPANY
Nghi Son Refinery and Petrochemical Limited Liability Company (NSRP) was established by investors including Vietnam Oil and Gas Group (25.1%), Kuwait Petroleum International Company (KPI) (35.1%), Idemitsu Kosan Company (IKC) (35.1%) and Mitsui Chemical Company (MCI) (4.7%) under the Joint Venture Contract signed on April 7, 2008. Nghi Son Refining and Petrochemical Co., Ltd is the investor of the Nghi Son Petrochemical Complex project.
8. LG ELECTRONICS VIETNAM HAI PHONG CO., LTD
LG Electronics Vietnam Hai Phong (LGEVH) is a company with 100% capital from Korea. In September 2013, the company was established with an investment capital of USD 1.5 billion. It is located at Lot CN2, Trang Due Industrial Park, Le Loi Commune, An Duong District, Hai Phong City, Vietnam. LG Electronics Vietnam Hai Phong’s products such as vacuum cleaners, washing machines, mobile phones and in-car audio-visual equipment are exported to 45 markets around the world.
9. VIETNAM AIRLINES JSC
Vietnam Airlines JSC was established on May 27, 1995 on the basis of combining 20 enterprises operating in the aviation service business, taking Vietnam Airlines as the core.
Despite the fierce competition in the aviation market, in 2018, the revenue of Vietnam Airlines Corporation (Vietnam Airlines) was over VND 100,000 billion, and its profit before tax was VND 2,012 billion.
10. FORMOSA HA TINH STEEL CORPORATION
Formosa Ha Tinh Steel Corporation is the investor of the Integrated Steel Complex and Son Duong Formosa Vung Ang Ha Tinh port. The registered investment capital of the project in phase 1 is USD 10.548 billion.
According to the Management Board of the Economic Zones in Ha Tinh, there are 24,000 employees from 31 countries and territories working in this plant. Its revenue in 2018 was USD 2.77 billion.
→ Overview of business in Viet Nam
Vietnam has risen to the top in international trade and has become a very attractive target for international investments. A young, dynamic population and an advanced qualified workforce help Vietnam form the most dynamic economic clusters.
Vietnam has a pro-investment policy. Different investment incentives and treatment rates apply to different industry groups and geographic groups. Incentives include exemption or reduction of corporate income tax for a number of years, land rent, exemption from import tax on capital goods, deferred payment of VAT, and more.
Efforts to improve the investment environment of the Vietnamese government
Investment license is valid for up to 50 years, renewable for another 50 years. The Foreign Investment Agency (fia.mpi.gov.vn) is the central licensing agency that issues licenses for a certain type of investment. With the support of investment departments in 63 provinces and cities nationwide, ready to help foreign investors. In some cases, the investment license must be approved by the Prime Minister.
Investment in Vietnam can be made directly or indirectly through the purchase of shares. The current process of equitization of State-owned enterprises in Vietnam is creating opportunities for foreign investors to participate in a number of sectors that are monopolized by the state.
Business opportunities in Vietnam
Statistically, Vietnam is changing step by step thanks to strong economic growth, ongoing reforms and a large population of 93 million – half of whom are under 30 years old – combined to create the environment. Trade is dynamic and growing rapidly. Sales of equipment, technology and consulting and management services associated with growth in Vietnam's industrial and export sectors and implementation of major infrastructure projects continue to be a source of commercial activity. commercial.

Many industries are suitable for foreign investors
1. Construction and building materials
Construction speed in Vietnam is very large. Especially in megacities, with high density of construction of streets, houses, and infrastructure.
You can start in Vietnam selling construction and construction materials. There are many building materials that you can sell, such as cement, roofing materials and home decorations. You can also start a business in the construction services sector such as painting services, plumbing, home decor, home repairs, HVAC installation and repair, and more. This is an opportunity for investors to create a market for themselves.
2. Agricultural Products Processing
Agriculture is gradually becoming the most important economic sector of Vietnam. Although agriculture still employs more than half of the population and the manufacturing sector accounts for only 8% of total employment, the output value of both manufacturing and services surpassed that of agriculture in the early 1990s. Some of Vietnam's key agricultural industries are coffee, paddy rice, pepper, sugar cane, etc.

Real estate tends to be heavily invested
3. Real Estate
Another lucrative business you can start in Vietnam is selling/buying houses and structures for sale. Due to the large number of foreigners and immigrants entering Vietnam, real estate is an unfortunate business. You can buy second hand items to repair and sell. You can rent office blocks or rent a small apartment.
However, investing in real estate requires a lot of money, so real estate is an expensive business. As an investor, this is not an unreliable situation and you still have the opportunity to run a real estate business, a property manager or a real estate agent. You can pay for this service.
Land policies and laws in Vietnam do not allow foreigners to own land in their name. Therefore, if investors want to develop a plan in this field, they need to grasp the necessary legal provisions.
4. Beauty and cosmetics
According to market research firm Mintel, the cosmetic and beauty retail market in Vietnam is expected to reach $1.7 billion per year, but in 2018 this figure could reach $2.35 billion. This market is relatively small, but as most countries move into the middle income group, the growth of most beauty and body care categories will continue to expand over the next decade. This is a great opportunity for investors to look at the cohesion of this business sector. When the demand for cosmetics increases, foreign companies can use natural spices to produce and sell cosmetics in Vietnam.
5. Car business
The car business is attracting investment in Vietnam. People with travel needs need high security. According to the law, including workshops, warehouses, equipment, tools, human resources, quality management systems, fire prevention and fighting mechanisms, environmental protection, safety and hygiene requirements, labor and maintenance facilities.
.jpg)
Threats in doing business in Vietnam
1. Intellectual property (IP)
Intellectual property rights are territorial, which means that intellectual property rights are protected only in the country of registration. Therefore, you should consider registering your IP rights (if necessary) in all of your export markets.
According to the 2018 Global Competitiveness Report of the World Economic Forum, Vietnam ranks 77th out of 140 countries in intellectual property protection.
Vietnamese law still has many loopholes in protecting intellectual property rights
Vietnam already has a set of rules to protect intellectual property rights. However, the implementation is still not robust, so you need to take steps to protect your IP before exporting.
Trademarks, designs, patents and copyrights are basic forms of intellectual property protection under Vietnamese law and are all governed by law. Common law allows one person to protect the transfer of goods and services from another person, and to protect confidential information or trade secrets.
Firms in certain industries are encouraged to research information on IP issues relevant to them. It is necessary to take precautions early when intending to penetrate the Vietnamese market.
2. Cybersecurity
Vietnam's new cybersecurity law, effective January 1, 2019, places requirements on data location, business operations, as well as storage and verification of users' information.
The law forces companies to provide information to Vietnamese authorities upon request and to block certain content within 24 hours. Applications and detailed application instructions remain approved.
If you plan to provide services to customers in Vietnam through telecommunications networks or the Internet (e.g. social networks, search engines, online advertising, broadcasting, websites/e-commerce). computer, voice/text Internet (OTT services), cloud services, online games and online applications), you will receive legal advice on compliance with the law.
3. Natural disasters
Tropical waves can occur on the east coast, usually from May to November, although they can occur outside of this time period. As a result, rainfall and strong winds can cause flooding and disrupt travel.
You should keep an eye on approaching storms on the website of the National Center for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasting.

Natural disasters often occur in Vietnam
Localized floods, flash floods and landslides are relatively common as Vietnam's tropical climate produces large amounts of rainfall in a short time. You need to be very careful when walking in rural and mountainous areas.
4. Tax policy in Vietnam
Although Vietnam's complex tax system is being reformed, there are still 10 types of corporate taxes to be paid each year. Other taxes also include VAT and social insurance.
Through these reforms, the Government of Vietnam intends to simplify all tax calculation and declaration procedures, remove confusing tax issues, and create a favorable business environment.
The authorities also have to do a lot of work related to improving tax reporting technology such as electronic tax return.
5. Most documents are in Vietnamese
All reporting and filing procedures, including permits, must be written in Vietnamese. Documents in English or other languages must be translated into Vietnamese through certified translations at the Court of the host country. It doesn't stop there. After that, the notarized translation document must be certified by the Vietnamese embassy.
Whether you're planning to invest in Vietnam or have been doing business for a while in Vietnam, get the support you need to manage the growing economy during unexpected circumstances. It is very important to move forward.
☆ Experts give advice on doing business in Vietnam
Starting a business in Vietnam can be challenging, especially if you are new to the market in this country. Here are the tips of experts on doing business in Vietnam. From there, it helps you quickly start operating a company in Vietnam and create value.
Every entrepreneur has his own direction for his business. For some, it is a very long and thorny process. For others, the business step is extremely favorable. If you are intending to invest effectively in the Vietnamese market, please consult experts in the field of legal, socio-economic and financial situation in Vietnam nowadays.
Advice on the hottest business in Vietnam
Most of the normal investment and business lines that Vietnam has fully liberalized are regulated to allow investors to set up foreign companies in Vietnam as individuals or in Vietnam. be an individual or corporate investor without restrictions. However, there are still some business lines with special conditions that have specific investment requirements regarding the investment status of an individual or a company, which can be determined by a combination of investment conditions. Commitment to open the market of Vietnam and the provisions of Vietnamese law, if any.
You can do business in many different industries in Vietnam
Regarding the provisions of law related to business lines, foreign investors are allowed to do any business that is not prohibited by law. In addition, there are certain occupations that must be met in order to register a business. Foreign investors can refer to the National Business Code System, also known as the CPC.
Check out some attractive businesses in Vietnam nowadays:
-
Textiles: Due to the fact that textile items are among the most exported in Vietnam, any entrepreneur who wants to start this business is sure to make a huge profit .
-
Building materials: Our business recommendations are based on forecasts about the promising future of the construction industry in Vietnam.
-
Restaurant and cafe chains: Vietnam's young population always creates favorable conditions for the F&B industry to operate stably and sustainably. Try investing in this field if you want to find long-term business opportunities in Vietnam.
-
Bar, beer, pug, club: This business is always favored by foreign investors because the formula for developing bars in Vietnam still lacks ideas for innovation. Meanwhile, foreign investors have many advantages to set up a new bar and gain market share in Vietnam.
Lost and found bar in Ho Chi Minh City invested by foreigners
Regulations of Vietnamese law on investment capital
Investment capital includes two main types: equity capital and debt capital, in which equity capital must account for at least 20% of total investment capital. Investors who want to establish a company in Vietnam must obtain an investment certificate from a licensing agency. For investment projects that are not subject to investment decisions, the general time to issue investment certificates is 15 days, but in practice, the licensing time is often longer, depending on the consultation process and assessment by the relevant authorities.
Except for some investment fields or conditional business lines, the current law does not stipulate the minimum capital level to establish a company in Vietnam. Based on the experience of long-term experts, in order for the process of applying for an investment certificate to go smoothly, investors need to consider the amount of capital sufficient to successfully implement the set business goals.
Vietnamese law has very specific regulations on investment capital
Register a business location according to Vietnamese law
The head office of the company, which is the contact point here, must have a specific and easily identifiable address, including: house number, street name (hutong) or name of commune, ward, township, district, district, town, etc. town or province or city. , province, city, province, city directly under the Central Government.
Head office is an extremely important factor for every business, especially when building a company. Finding a suitable address to locate the head office is also a big obstacle for foreign investors when there is not much information about the location in Vietnam. Therefore, foreign investors should choose locations that are allowed to lease and design - build. Therefore, the lessor has all documents proving ownership, right to lease or sublease (if any).
Advice for legal representatives
According to the provisions of the Enterprise Law, the legal representative of an enterprise is an individual who exercises rights and obligations arising from enterprise transactions on behalf of the enterprise, and represents enterprise to enterprise. The plaintiff, the defendant, the relevant rights and obligations before the arbitration, the status of the court, and other rights and obligations stipulated by law.
In addition, LLCs and joint stock companies can have more than one legal representative, which helps the company integrate faster and capture all business opportunities. Moreover, this regulation will increase the initiative of enterprises when going through industrial and commercial registration procedures, save time and cost, especially large enterprises with a large number of representatives, and make them more legal.
Tax obligations of foreigners business investing in Vietnam
Tax liability is one of the basic obligations of any company, not excluding the nationality of the investor. Therefore, every year Vietnamese companies have to pay various taxes and fees. For example: license fee (based on registered charter capital); corporate income tax on profits; VAT reporting and payment. Depending on the business and investment sector, companies in Vietnam may also be subject to taxes such as export tax, import tax, etc.
Vietnam has committed to open markets, as well as corporate income tax in some industries or many investment incentives for investment in areas with socio-economic conditions and difficult society.
Compliance with tax obligations in Vietnam
Business lines banned from foreign investors
Vietnamese law has not really dealt with cases of non-compliance with regulations on business lines and industries. However, in order to avoid troubles in the process and minimize the risk of having to work with investigators and the court, we recommend that you do not choose the following areas for investment and business creation:
-
Trading in goods and services on the list of goods and services monopolized by the State in the field of commerce.
-
Any kind of news activities and news interview activities.
-
Investigative and Security Services.
-
Judicial administrative services, including judicial professional services, bailiff services, property auction services, notary services and asset management services.
-
Service of sending workers to work abroad under contract.
-
Investing in the construction of cemeteries and cemetery infrastructure, transferring land use rights related to infrastructure.
-
Directly from the domestic waste collection service.
-
Producing and trading in weapons, explosives and supporting tools.
-
Import and dismantle old ships.
-
Public postal service.
-
Trade transshipment of goods.
-
Trading in temporary imports for re-export.
-
Exercising the right to export, the right to import, and the right to distribute with respect to goods on the list of goods for which foreign investors and foreign-invested economic organizations are not allowed to exercise the right to export or to import , distribution rights.
-
Producing military supplies and equipment; trading in military equipment, military equipment of the armed forces, military weapons, equipment, technology, weapons, special vehicles of the army and police, components, parts, spare parts, supplies, equipment special equipment and expertise in their manufacture;
-
Business Industrial Property Agency Services and Intellectual Property Assessment Services.
-
Establish, operate, maintain and maintain maritime signaling services, waters, bodies of water, public waterways and waterways; surveying services of water bodies, waters, public waterways and waterways, serving the issuance of maritime notices; services of surveying waters, seaports, waterways and waterways, Drawing and publishing charts; develops and publishes documents and publications on maritime safety.
-
Regulatory services to ensure maritime safety in sea areas, waters and public waterways; maritime electronic information service.
-
Services of investigation, assessment and development of natural forests (including exploitation and hunting, trapping of rare and precious wild animals and management of genetic funds of crops, livestock and agricultural microorganisms).
-
Research and use genetic resources of new livestock and poultry breeds before the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development approves and appraises them.
-
Business travel services, except international travel services serving international tourists to Vietnam.
List of occupations that foreigners are not allowed to do business in Vietnam
How will foreigners be penalized if they violate Vietnam's investment law?
For situations where civil transactions are violated, investors may be subject to administrative sanctions and other related sanctions. For violations of criminal law, investors will be handled according to Vietnamese law on the basis of compliance with international law and Vietnam's extradition agreement with the country where the investor violates the citizen.
Conclusion: Is Vietnam still an attractive investment station for foreign investors?
The world is always changing and unpredictable. Epidemics, natural disasters, wars, competition, etc. are likely to continue, so each country has its own adaptive way to survive and develop, especially those with economies of scale. Vietnam's economy in general is still small, still dependent on the outside and globally dependent.
Vietnam considers foreign capital as one of the important resources, the driving force for economic development, international cooperation and participation in the global value chain. Efforts should be made to improve the investment environment and create favorable conditions for foreign companies to do business and long-term production in Vietnam.
The final advice when doing business in Vietnam is to quickly seize the opportunity, seek legal support and participate in this vibrant market.
FAQs
Why Vietnam is an attractive destination for foreign investors ?
Advise:
International integration
Vietnam has demonstrated its commitment to international integration and affirming a new role, image, prestige, and position in the international arena. In more than three decades of renovation and integration, Vietnam has signed 15 FTAs. In the past five years, Vietnam has signed several new-generation FTAs including CPTPP, EVFTA, UKVFTA, RCEP.
Strategic geographic locations
Vietnam is located in the center of South East Asia, sharing boundaries with the Pacific Ocean, Gulf of Thailand, Laos, Cambodia and China Vietnam has over 3,000 km long coastline, near main international shipping and trading routes.
Competitive labor force
Workforce is an advantage of Vietnam with a working-age population of over 54 million, a steadily increasing proportion of trained workers, and competitive costs compared to neighboring countries.
Political stability
Vietnam is one of the more politically stable countries in South East Asia. Alongside maintaining the one-party state system, its main aim is economic growth.
Improving investment climate
Vietnam continues to welcome FDI and foreign companies play an important role in the economy. Business environment continues improving by new laws streamlining the business registration processes. The country therefore attains high ranking in business registration procedures and ease of doing business. Vietnamese Government prioritizes the infrastructure improvement to attract more FDI.
Dynamic economy
Vietnam is one of the fastest growing economies in the Asia region. GDP growth rate: 6.78% (avg. 2016 – 2019) Population: 97.58 million (avg. 2020)
Law on Tax Administration in Vietnam ?
Advise:
In recent years, the Ministry of Finance (MOF) and the General Department of Taxation have made efforts to reform and simplify tax administration policies and procedures. From 1 July 2020, most elements of the new Law on Tax Administration No. 38/2019/QH14 came into force (except for regulations on electronic documents and invoices of this law which will come into force from 1 July 2022). The new law brings some additional changes that are considered business friendly. Conflict can be avoided, according to the new law, since no administrative penalty and late tax payment is imposed if taxpayers complied with local tax authorities’ guidance which led to a deficit of tax liability or a surplus tax refund. There will be more time for individual taxpayers to comply with their obligations since the deadline of Personal Income Tax Finalization is extended by one month to the last day of the fourth month after the calendar year end. The old law regulated but did not have specific guidance on the use of electronic invoices and electronic documents. The new law provides detailed guidance on the usage of electronic invoices. Under the new law electronic invoices will be mandatory for most enterprises and the use of electronic documents will be promoted. Using electronic invoices and electronic documents should be less time-consuming and more accurate.
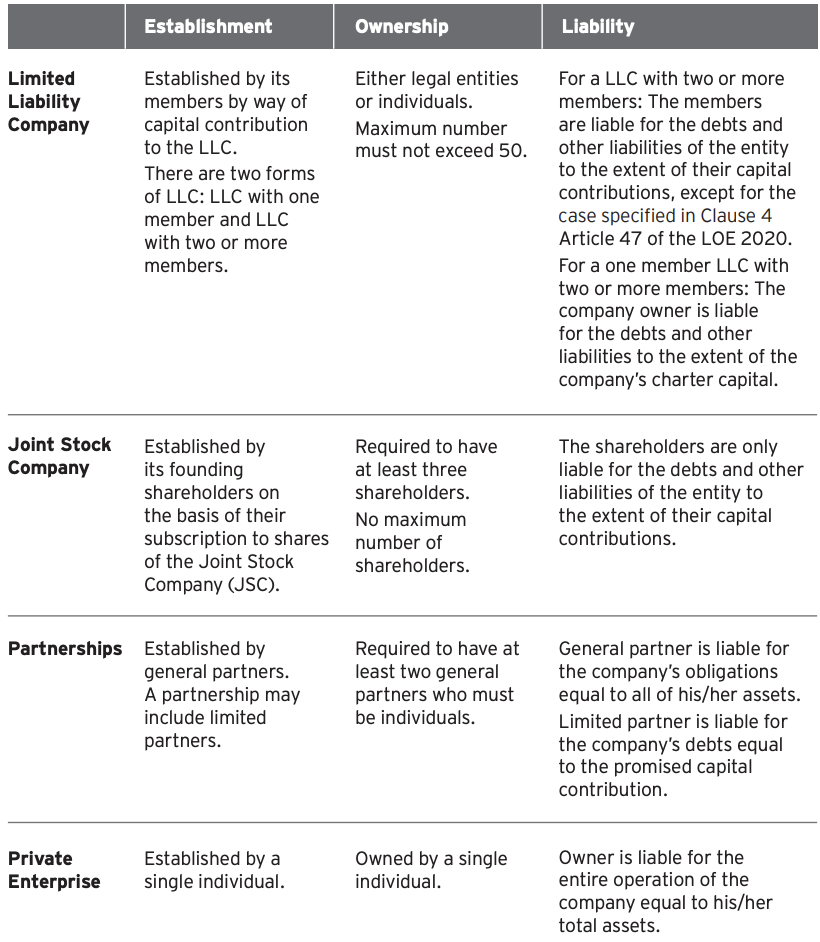
Forms of enterprise in Vietnam ?
Advise:
Forms of enterprise in Vietnam bellow
Tax regime in Vietnam ?
Advise:
Taxation In the majority of cases, tax liability is self-assessed meaning that the taxpayer is responsible for determining the amount of tax it must pay. Following self-assessment and payment, the taxpayer will be subject to an audit or inspection by the tax authorities. Audits usually take place every one to five years. Any reassessments under the audit process will either be settled by the taxpayer or the taxpayer may go through one of the appeal mechanisms. Standard process for taxpayers in determining tax obligations Source: Decree No. 125/2020/ND-CP, dated 19 October 2020, issued by the Government; Article 8, Decree No. 126/2020/ND-CP, dated 19 October 2020, issued by the Government; Law on Tax Administration No. 38/2019/QH14, dated 13 June 2019, issued by the National Assembly of Vietnam (1) Calculation (4) Resolve impacts (2) Declaration and Payment (3) Audit/Inspection Tax liability calculation Additional tax & penalty payment; or Initiate lawsuit Tax returns submission Tax liability payment On regular basis (one to five years at a time)










1 comment
Lee Mei
How to start a business in Viet nam as a foreigner?
Send comment